Marcella Soto had four children by the time she was 22 and was on and off welfare during the years they were growing up. By 2018, she was working a government job in California when she was charged with six counts of welfare fraud. Unable to prove that she had not misreported her income many years earlier, she pleaded guilty to a single felony count.
Soto was sentenced to the maximum probation term — five years — and was required to check in with a supervisor every month. Because of the conviction, she lost her job; because of the conditions of her probation, she was unable to travel to Texas to attend the birth of her first grandchild.
Being sentenced to probation put Soto in the largest group of people in America’s criminal justice system. About 1.9 million US residents are behind bars, and 3.7 million are being monitored while they are on probation in lieu of incarceration or on parole after being let out of lockup.
Probation and parole — collectively known as community supervision — were originally conceived as alternatives to incarceration, allowing convicted criminals to be rehabilitated under supervision. But criminal justice leaders say the practices have strayed from that original mission and become so ineffective that, ironically, they contribute to America’s overcrowded prisons. These critics call for an overhaul of community supervision, including shorter terms and more support for rehabilitation. In some states, new laws are making headway.
“Nearly half of the people going into jails and prisons are coming in from a failed and broken probation and parole system,” says Robert Rooks, chief executive officer of Reform Alliance, a nonprofit advocacy group. “So if you want to address mass incarceration in this country, you have to address the phase of probation and parole.”
Changing goals
Parole and probation were originally intended as opportunities to rehabilitate offenders through support, such as help finding jobs or housing. This focus on rehabilitation began to recede in the 1970s when a tough-on-crime public sentiment emerged. Parole and probation morphed instead into systems of surveillance — intense scrutiny over long periods of time — supposedly in support of public safety.
With this shift, critics say, community supervision became a form of “net-widening,” keeping people in the criminal justice system rather than easing them back into society. “In many people’s minds, this is a good thing you get instead of going to prison,” says Vincent Schiraldi, a former commissioner of the New York City Department of Probation. “But this is a bad thing. It’s got a lot of bad outcomes for a lot of people.”
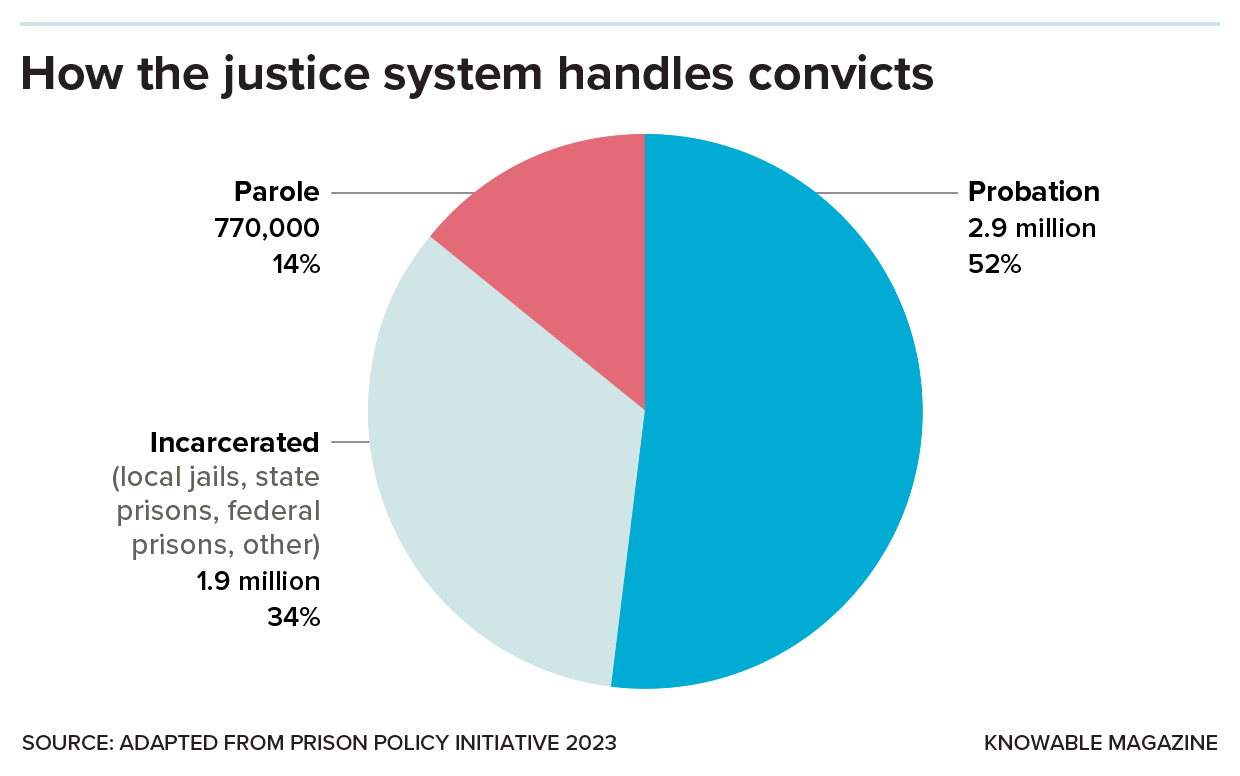
Most people convicted of crimes are sentenced to probation, and a smaller number are on parole after serving time. Only 34 percent of convicts in the US were actually in prison for their crimes in 2023.
For instance, probationers must comply with a growing, often complex list of conditions — which typically number 18 to 20 — that can be difficult to meet, Schiraldi says. Avoiding contact with anyone who has a criminal conviction is hard if an offender’s family or support network includes convicts; returning home by curfew can interfere with keeping a job. In Pennsylvania, where a released prisoner could be on parole for the rest of their life, probationers are prohibited from leaving the state, which means an Uber driver on probation in Philadelphia cannot drive into the suburbs that spill into Delaware.
“That right there shows you that our current policies are arbitrary, unnecessary and hinder people’s ability to do the things they need to do to become stable, get back to work and provide for their families,” Rooks says. “And that’s the opposite of what probation and parole should be doing.”
Indeed, a 1993 survey of people imprisoned in Texas found that 66 percent said they would choose incarceration over a 10-year probation sentence. When Schiraldi was New York City’s probation commissioner in 2010, he saw a woman give up her probation, choosing instead to go to Rikers Island jail, because she was unable to find childcare that she needed for her probation check-ins, where children were not allowed.
All these problems might be acceptable if probation and parole were meeting the goal of reducing incarceration without leading to more crime. Schiraldi and two colleagues examined that proposition in the 2023 Annual Review of Criminology — and concluded that they are not.
Community supervision clearly fails at reducing incarceration. The more people living under probation and parole in one year, the higher the incarceration rate the following year, according to work by Schiraldi and his coauthors. That reflects, in part, the fact that failing to comply with terms of supervision can mean a ticket to jail. In 2017, revocation of parole or probation accounted for 45 percent of prison admissions, and in 20 states, more than half of those revocations were not for new crimes, but for violating the terms of supervision.
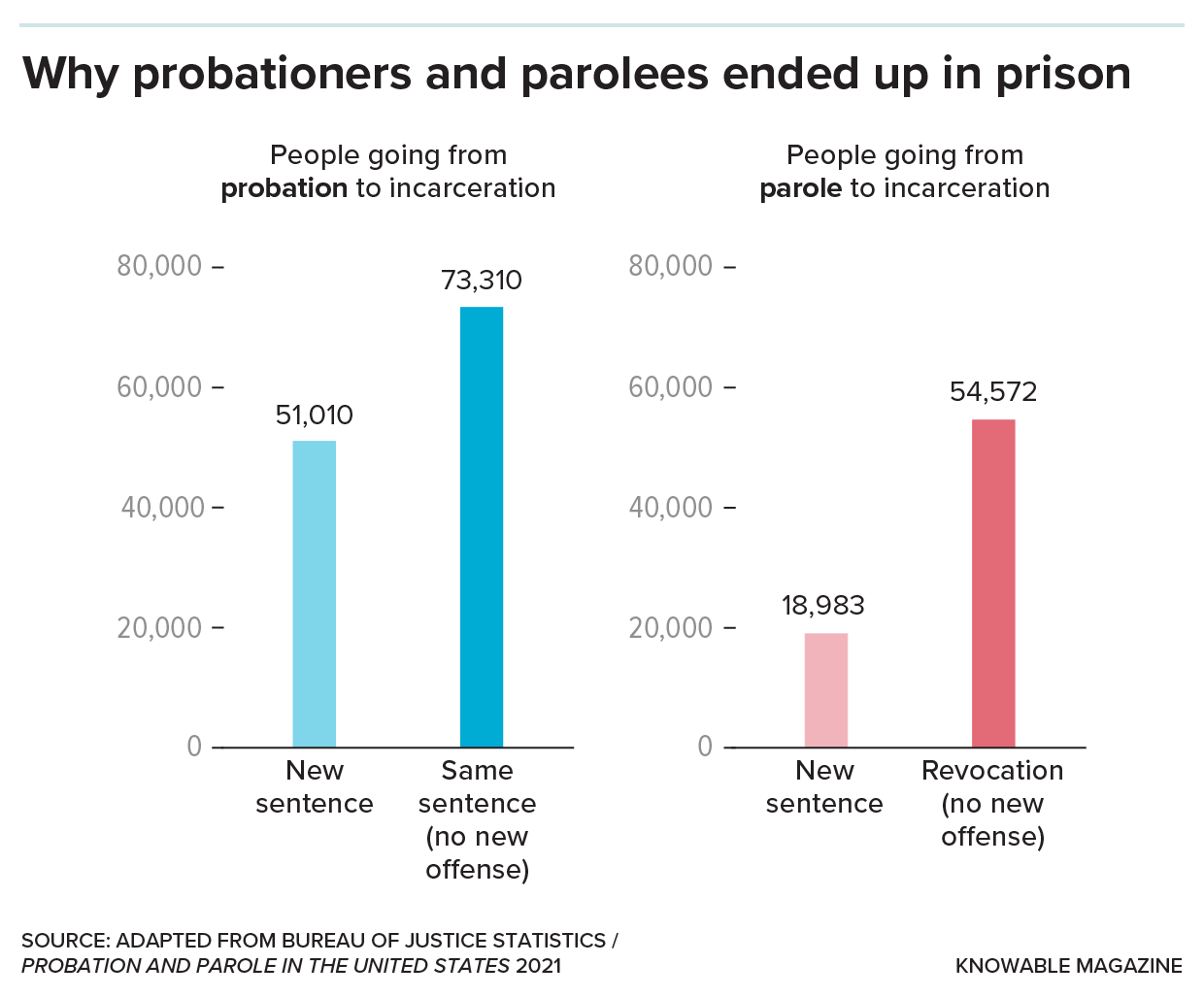
Most convicts whose parole or probation is revoked end up incarcerated not because they commit new crimes, but because they violated the terms of their release, these US data from 2021 show.
The evidence on public safety is more equivocal. If releasing people on parole and probation poses a risk of further crime, then the more people released on supervision in a given year, the higher the crime rate would be in the following year. But that isn’t the case. Overall, a state’s probation, parole and total supervision rate in one year does not predict the state’s rate of index crime — a term that includes violent crime plus several kinds of property crimes — in the following year.
For parole alone, however, the researchers found that the more parolees in a given year, the more violent crime the next year. That implies that parole could be risky.
But looking at the issue in a different way, Urban Institute researchers showed no clear risk, as well as no benefits, from parole. The team reviewed long-term Bureau of Justice Statistics data on 38,624 prisoners from 14 states released from prison in 1994 and found that parole supervision does not substantially affect recidivism or public safety. People simply released from prison without supervision were no more likely to be rearrested than those who were required to complete a term of parole after their sentence, they found — though people paroled before the end of their prison sentences did have lower rearrest rates.
Other evidence also suggests that recidivism may arise early, so long supervision terms may not be helpful in reducing crime. For example, among felony probationers in Oregon who were rearrested within three years of their probation, 69 percent were arrested in the first year, according to data from the Oregon Criminal Justice Commission. That suggests that the early months of probation and parole may be a critical period for helping offenders change their behavior and connecting them with community services.
In addition, making community supervision less punitive has been shown to work. One in-depth study of 283 offenders in an intensive supervision program in Wyoming compared the effect of rewards, such as praise or removal of electronic monitoring, to punishments, such as reprimands or tightened curfew. The offenders were most likely to complete their supervision successfully if they received at least four times as many rewards as sanctions.
Several studies show that employment for people under supervision helps to reduce recidivism. A transitional job program in New York City for people leaving prison led to a 9 percentage-point reduction in any type of recidivism (arrest, conviction or jail) over the three-year follow-up period compared to results with parolees not in the program. That suggests that supporting employment — rather than making it difficult by travel restrictions — is a good idea.
Evidence like this led Schiraldi and Barbara Broderick, former chief probation officer for Maricopa County in Arizona, to launch Exit, a group made up of current and former community supervision leaders, victims, prosecutors and others who want to see probation and parole downsized and returned to their original purpose of rehabilitation.
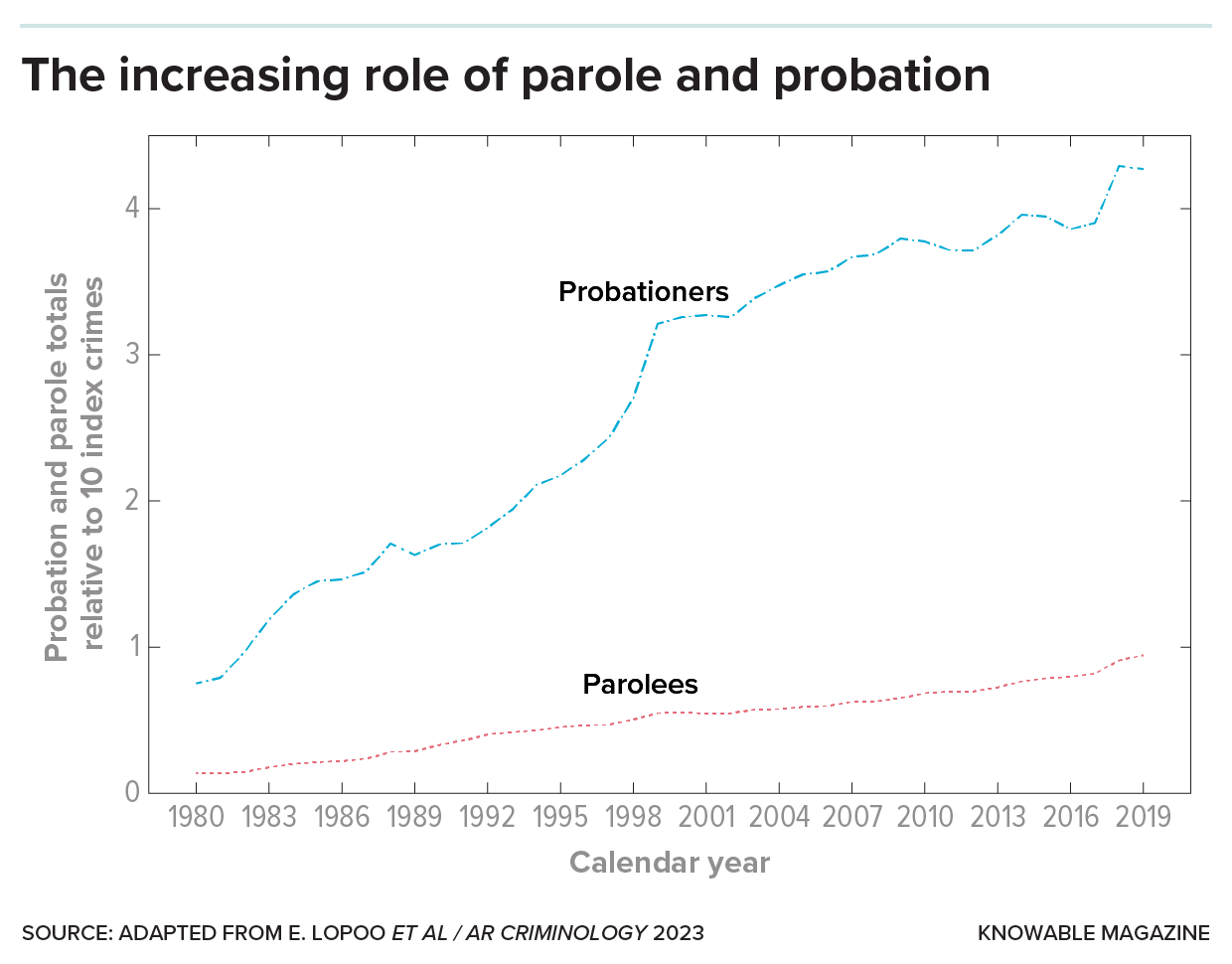
Correctional systems are relying increasingly on parole and probation. This graph shows the number of probationers and parolees, relative to the rate of “index crimes” (violent crimes plus some property crimes) for each year from 1980 to 2019.
Among other aims, they want people on probation to be able to earn time off supervision if they maintain good behavior and achieve milestones like graduating from high school or keeping a job. They want the money saved from reduced supervision to be invested in community-based services that support people on probation or parole. They want incarceration for technical violations to be eliminated in favor of more and better supportive services that help people on parole and probation reintegrate into their communities.
A better way
Some of the greatest progress has been in California, where a series of reform laws since 2007 has transformed the incarceration and community supervision landscape, Rooks says. The reforms reduced prison sentences and supervision periods for many offenses and encouraged the use of evidence-based supervision strategies such as needs assessments, tailoring the intensity of supervision to a probationer’s risk of recidivism, and increased referrals to counseling, substance abuse treatment and employment services.
“In many people’s minds, [probation] is a good thing you get instead of going to prison. But this is a bad thing.”
— VINCENT SCHIRALDI
Because of these and other reforms, the number of Californians under community supervision fell from 477,733 in 2006 to 306,500 in 2020, a decrease of 42 percent. Meanwhile, reported crime declined by 7.4 percent during those years — and a study found the reforms had no measurable effect on violent crime, suggesting that less-punitive treatment did not increase crime.
Another California reform, passed in 2020, limits most probation sentences for misdemeanors to one year and most probation sentences for felonies to two. The change is projected to reduce the number of people on probation by a third, avert more than 48,000 prison stays because of technical violations and save the state $2.1 billion over five years, according to calculations by Recidiviz, a nonprofit organization that compiles and analyzes data to support criminal justice reform.
The saved money could be used to address the root causes of criminal behavior. For example, in early 2021 the El Dorado County Probation Department opened a house where probationers experiencing or at risk of homelessness can live and receive support services. “It allows you to free up the resources to give people the help that they need, which is what probation really should be about,” Rooks says.
When Soto learned about California’s new probation term limits in 2021, her probation officer did not support reducing her probation sentence, so Soto went to court. “The judge right away said, ‘You know what? I got her report. She’s never been in trouble and she’s working,’” she recalls. “And they let me off three years early.”
Now living in Oklahoma, where she works as a warehouse manager and lives with her daughter and the grandson whose birth she missed, Soto remembers that day. “I could travel and be free, and I didn’t have to worry about the visitation from the officer,” she said. “I was able to get my life back.”