She ain’t scary, she’s my mother
Elaborate courtship, devoted parenthood, gregarious nature (and occasional cannibalism) — earwigs have a lot going for them
Support sound science and smart stories
Help us make scientific knowledge accessible to all
Donate today
Few people are fond of earwigs, with their menacing abdominal pincers — whether they’re skittering across your floor, getting comfy in the folds of your camping tent or minding their own business.
Scientists, too, have given them short shrift, compared with the seemingly endless attention they have lavished on social insects like ants and bees.
Yet there are a handful of exceptions. Some researchers have made conscious career decisions to dig into the hidden, underground world where earwigs reside, and have found the creatures to be surprisingly interesting and social, if still not exactly endearing.
Work in the 1990s and early 2000s focused on earwig courtship. These often-intricate performances of attraction and repulsion — in which pincers and antennae play prominent roles — can last hours, and the mating itself as long as 20 hours, at least in one Papua New Guinea species, Tagalina papua. The females usually decide when they’ve had enough, though males of some species use their pincers to restrain the object of their desire.
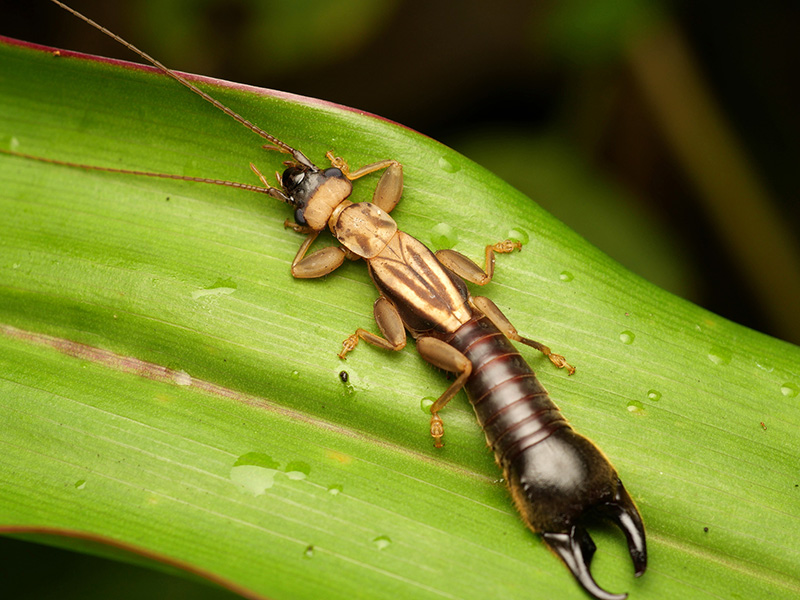

InTagalina papua, an earwig species from Papua New Guinea, mating can last up to 20 hours. That is the longest documented in any earwig species, but few have been studied in detail.
CREDIT: PHILIPP HOENLE / iNATURALIST
Males of the bone-house earwig Marava arachidis (often found in bone meal plants and slaughterhouses) are particularly coercive, says entomologist Yoshitaka Kamimura of Keio University in Japan, who has studied earwig mating for 25 years. “They bite the female’s antennae and use a little hook on their genitalia to lock them inside her reproductive tract.”
Size matters
Female earwigs collect sperm in one or more internal pouches and can use it to fertilize multiple broods, so they don’t need to mate again. The only thing most males can do is add their own sperm, but Kamimura has seen males of the pale-legged earwig Euborellia pallipes remove the sperm of other males using an elongated part of their peculiar penis.
It’s better if females can prevent this from happening, because they can be particular about the males they mate with. This may explain why, in some species, male and female genitalia have increased in size as part of a kind of evolutionary arms race in which males benefit from access to the pouch and females benefit from keeping them out. In the bristly earwig Echinosoma horridum, the male’s genitalia are nearly as long as the rest of his body, and the female’s genitalia almost four times as long as the rest of hers.
Fascinating though they are, the amorous adventures of earwigs weren’t what first caught Kamimura’s attention. Rather, he was intrigued by the female’s dedication to her offspring. “When I was a student, I accidentally disturbed an earwig caring for her eggs in our backyard,” he recalls. “She ran away but returned the next day. I was very interested, and I started to rear them.”
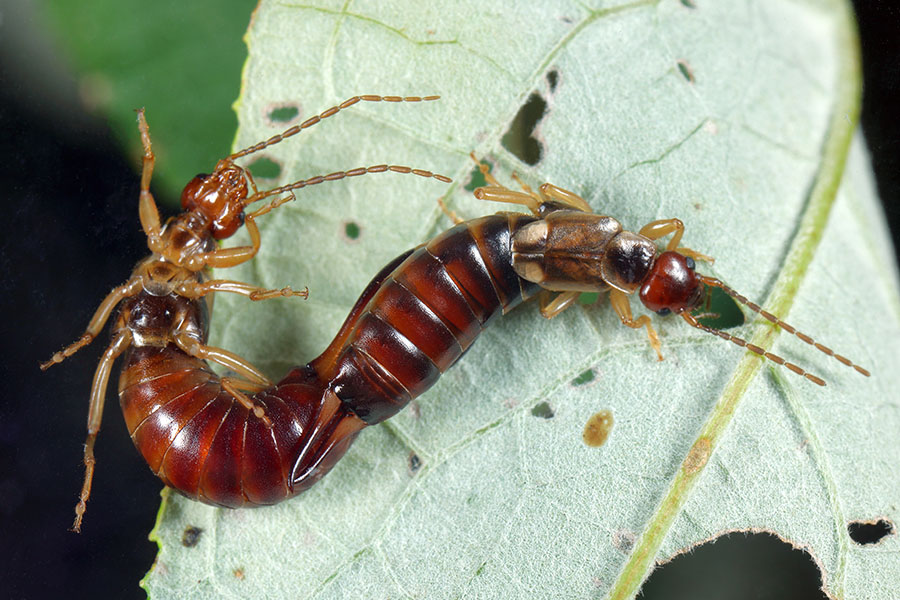

Two European earwigs. When, after lengthy courtship, a female is persuaded to mate, she will lift and twist the tip of her abdomen to allow the male to insert his sperm.
CREDIT: JAN VAN DUINEN / NATURE IN STOCK
Grow your own earwigs
The care that female earwigs provide to their eggs has also become the focus of study in Europe, where a surge of lab research on European earwigs — Forficula auricularia — was kick-started almost 20 years ago by entomologist Mathias Kölliker at the University of Basel, Switzerland. “Getting them to breed continuously over multiple generations was a big challenge,” he recalls. “The females did lay eggs, but they didn’t develop, and never hatched.”
It turned out that the eggs, which are laid in late fall and hatch in January, need the winter cold to start their development. So the scientists figured out a lab regimen that would chill but not kill the eggs. “That took us about two years,” says Kölliker.
In 2009, Kölliker hired entomologist Joël Meunier, who continues to study earwigs at the University of Tours in France and wrote an overview of the biology and social life of earwigs for the Annual Review of Entomology. Earwigs are high maintenance, he says. “If you work with fruit flies, you can breed 10 generations in a few months, but earwigs take much longer.… And they’re all kept in separate petri dishes — thousands of them — that we have to open twice a week to replace the food.
“I think this is one of the reasons few people work on them. But they’re very fascinating.”
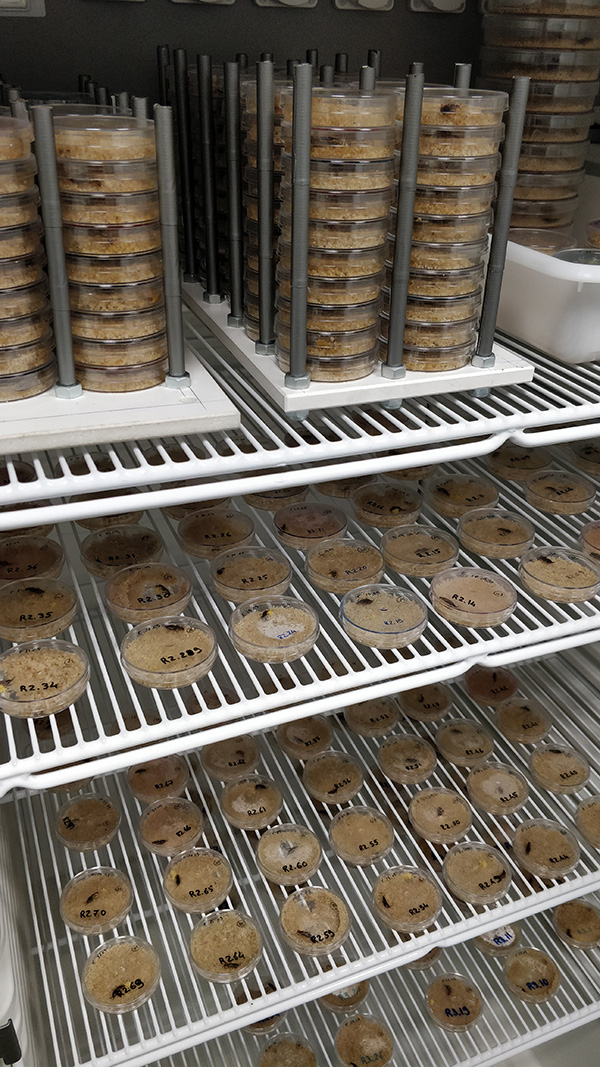

In the lab, earwigs are kept in thousands of petri dishes that have to be opened twice a week to replace the food. The complicated lab care may be one reason few scientists work with them.
CREDIT: COURTESY OF JOËL MEUNIER
Fending off males
The female’s careful egg-grooming has at least two important functions. First, she uses a small brush on her mouthparts to remove the spores of fungi that can kill the eggs. Secondly, as Kölliker, Meunier and colleagues found, she applies water-repellent hydrocarbons to keep them from drying out.
Males that attempt to approach the nest are aggressively chased away, and with good reason, says Meunier. “Once, when we were in the field in Italy to collect earwigs, we found a male and a female together with a clutch of eggs. We were quite excited: Wow, biparental care, cool! So we brought them to the lab. But what we actually observed was that the female was very stressed out, showing a lot of aggression towards the male, while the clutch size was continuously decreasing.”
Males, it turns out, love to snack on eggs, even ones that they fathered. To chase them off, females raise their abdomens to show off their pincers. If that’s not enough, they can use the pincers to hurt the male — even to cut him in half. (Scary as they look, the pincers can’t harm people at all, Meunier says.)
Earwigs can also spray each other with defensive secretions that may have antimicrobial properties too. “They often use those secretions when meeting others,” says Meunier. “Maybe it also prevents the spread of disease.”
As far as scientists know, these secretions are harmless to humans. But because they contain quinone derivatives, which are also found in substances like henna, they have some quirky side effects. “When you get a lot of it on your hands,” Meunier says, “they’ll turn blue, like a bruise, and these marks can last all week.”
The secretions smell quite pleasant, says Kölliker. “When I had a visitor in the lab, I would sometimes pick up an earwig and hold it under their nose. It’s a very nice odor, actually, kind of an earthy smell.” Kölliker’s cat was less appreciative when he tried it on her: “She immediately backed off,” he says.
Overbearing moms
Surprisingly, Meunier’s recent work suggests that earwig offspring may pay a price for their mom’s protectiveness. In European earwigs and several other species, although the nymphs that emerge from eggs can feed on their own after a couple of days, mothers usually stay with them for a few weeks after they hatch. Yet, at least in the lab, that does not seem to enhance the nymphs’ chances of survival.
“In the best case, the mother’s presence doesn’t change a thing,” says Meunier. “At worst, nymphs that grow up with their mother are less likely to reach adulthood and will become smaller adults.” It’s unclear why. But things may be different in the wild, where male earwigs or predators like spiders pose threats, making it safer to stay with mom.
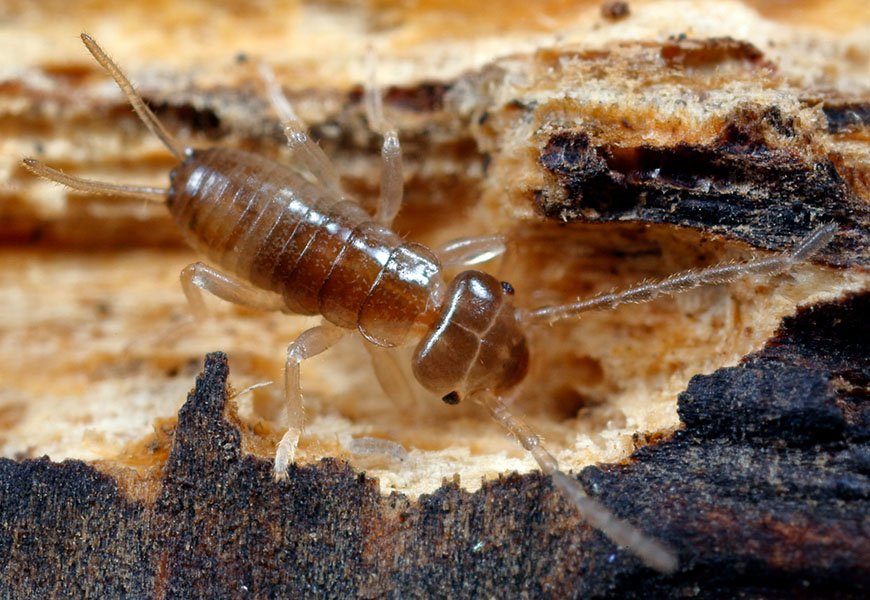

The nymphs that emerge from earwig eggs can feed on their own after a couple of days, but their mother will often stay with them for longer.
CREDIT: JAN VAN DUINEN / NATURE IN STOCK
The mother herself seems to benefit. Meunier has observed that as soon as the nymphs emerge, they eat the parasitic mites that often bother breeding females. And once they start foraging on their own, the feces they leave all over the nest may be food for their mother and help her to produce a second brood. The nymphs also feast on each other’s feces, sometimes straight from the source.
The voracious nymphs don’t stop there: They regularly eat each other, and nymphs of the hump earwig Anechura harmandi will almost always eat their mother. “It occurs in every family,” Meunier says, “and it helps the nymphs grow.”
Let’s get together
With all this aggression and cannibalism, you’d expect adult earwigs not actively seeking mates to avoid each other, and in many species, they do. Yet European earwigs regularly group together by the hundreds, sometimes mixing things up with other earwig species.
Recent work from Meunier’s lab showed that European earwigs that grew up in groups are more likely to look for company as adults than those reared in isolation, and females removed from these groups can get so stressed they are more likely to succumb to fungal infections.
“We have no idea why,” says Meunier. “Maybe it’s healthier to live together. Or maybe, they just like company.”
10.1146/knowable-111324-2
TAKE A DEEPER DIVE | Explore Related Scholarly Articles