Cracking the recipe for perfect plant-based eggs
Hint: It involves finding just the right proteins. With new ingredients and processes, the next generation of substitutes will be not just more egg-like, but potentially more nutritious.
Support sound science and smart stories
Help us make scientific knowledge accessible to all
Donate today
An egg is an amazing thing, culinarily speaking: delicious, nutritious and versatile. Americans eat nearly 100 billion of them every year, almost 300 per person. But eggs, while greener than other animal food sources, have a bigger environmental footprint than almost any plant food — and industrial egg production raises significant animal welfare issues.
So food scientists, and a few companies, are trying hard to come up with ever-better plant-based egg substitutes. “We’re trying to reverse-engineer an egg,” says David Julian McClements, a food scientist at the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
That’s not easy, because real eggs play so many roles in the kitchen. You can use beaten eggs to bind breadcrumbs in a coating, or to hold together meatballs; you can use them to emulsify oil and water into mayonnaise, scramble them into an omelet or whip them to loft a meringue or angel food cake. An all-purpose egg substitute must do all those things acceptably well, while also yielding the familiar texture and — perhaps — flavor of real eggs.
Today’s plant-based eggs still fall short of that one-size-fits-all goal, but researchers in industry and academia are trying to improve them. New ingredients and processes are leading toward egg substitutes that are not just more egg-like, but potentially more nutritious and better tasting than the original.
In practice, making a convincing plant-based egg is largely a matter of mimicking the way the ovalbumin and other proteins in real eggs behave during cooking. When egg proteins are heated beyond a critical point, they unfold and grab onto one another, forming what food scientists call a gel. That causes the white and then the yolk to set up when cooked.
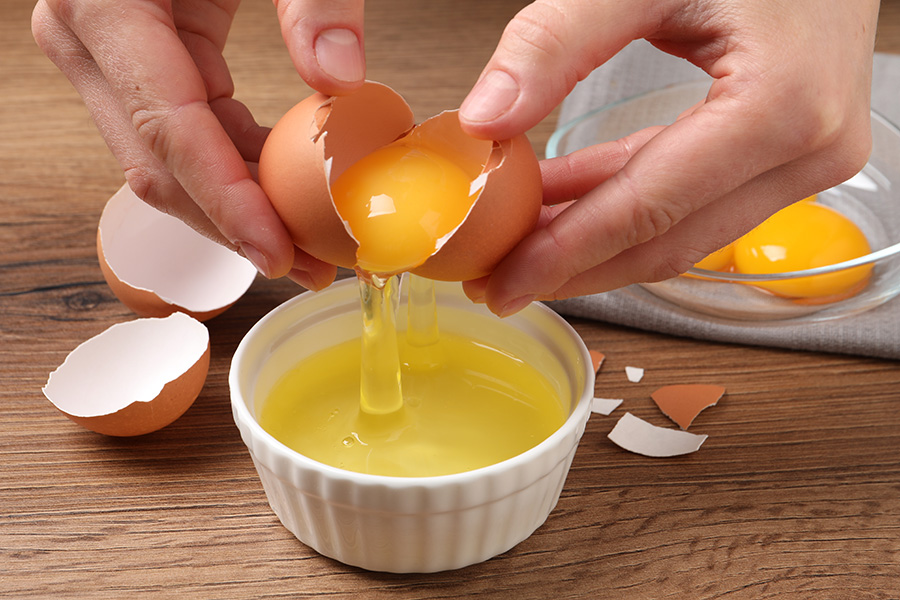

Eggs aren’t just for frying or scrambling. Cooks use them to bind other ingredients together and to emulsify oil and water to make mayonnaise. The proteins in egg whites can also be whipped into a foam that’s essential in meringues and angel food cake. Finding a plant-based egg substitute that does all of these things has proven challenging.
CREDIT: NEW AFRICA / SHUTTERSTOCK
That’s not easy to replicate with some plant proteins, which tend to have more sulfur-containing amino acids than egg proteins do. These sulfur groups bind to each other, so the proteins unfold at higher temperatures. As a result, they must usually be cooked longer and hotter than ones in real eggs.
To make a plant-based egg, food scientists typically start by extracting a mix of proteins from a plant source such as soybean, mung bean or other crops. “You want to start with what is a sustainable, affordable and consistent source of plant proteins,” says McClements, who wrote about the design of plant-based foods in the 2024 Annual Review of Food Science and Technology. “So you’re going to narrow your search to that group of proteins that are economically feasible to use.”
Fortunately, some extracts are dominated by one or a few proteins that set at low-enough temperatures to behave pretty much like real egg proteins. Current plant-based eggs rely on these proteins: Just Egg uses the plant albumins and globulin found in mung bean extract, Simply Eggless uses proteins from lupin beans, and McClements and others are experimenting with the photosynthetic enzyme rubisco that is abundant in duckweed and other leafy tissues.
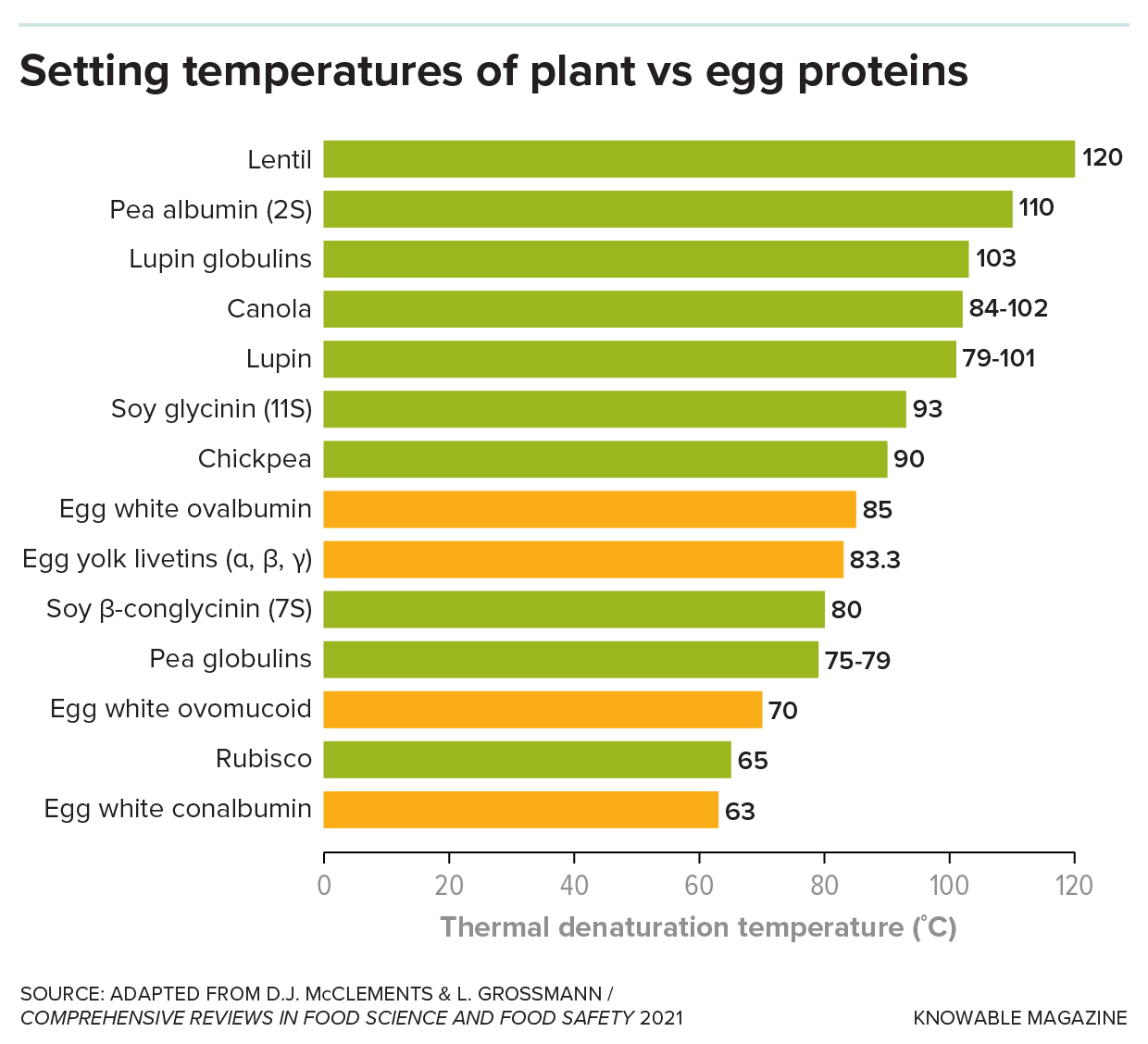
One reason that plant-based eggs don’t behave like real ones when cooked is that most plant proteins set, or denature, at higher temperatures. Choosing plant proteins that set at lower temperatures is an important first step in making a convincing egg substitute.
These days, food technologists can produce a wide range of proteins in large quantities by inserting the gene for a selected protein into hosts like bacteria or yeast, then growing the hosts in a tank, a process called precision fermentation. That opens a huge new window for exploration of other plant-based protein sources that may more precisely match the properties of actual eggs.
A few companies are already searching. Shiru, a California-based biotech company, for example, uses a sophisticated artificial intelligence platform to identify proteins with specific properties from its database of more than 450 million natural protein sequences. To find a more egglike plant protein, the company first picked the criteria it needed to match. “For eggs, that is the thermal gel onset — that is, when it goes from liquid to solid when you heat it,” says Jasmin Hume, a protein engineer who is the company’s founder and CEO. “And it must result in the right texture — not too hard, not too gummy, not too soft.” Those properties depend on details such as which amino acids a protein contains, in what order, and precisely how it folds into a 3D structure — a hugely complex process that was the subject of the 2024 Nobel Prize in chemistry.
The company then scoured its database, winnowing it down to a short list that it predicted would fit the bill. Technicians produced those proteins and tested their properties, pinpointing a handful of potential egglike proteins. A few were good enough to start the company working to commercialize their production, though Hume declined to provide further details.
Cracking the flavor code
With the main protein in hand, the next step for food technologists is to add other molecules that help make the product more egglike. Adding vegetable oils, for example, can change the texture. “If I don’t put any oil in the product, it’s going to scramble more like an egg white,” says Chris Jones, a chef who is vice president of product development at Eat Just, which produces the egg substitute Just Egg. “If I put 8 to 15 percent, it’s going to scramble like a whole egg. If I add more, it’s going to behave like a batter.”
Developers can also add gums to prevent the protein in the mixture from settling during storage, or add molecules that are translucent at room temperature but turn opaque when cooked, providing the same visual cue to doneness that real eggs provide.
And then there’s the taste: Current plant-based eggs often suffer from off flavors. “Our first version tasted like what you imagine the bottom of a lawn mower deck would taste like — really grassy,” says Jones. The company’s current product, version 5, still has some beany notes, he says.
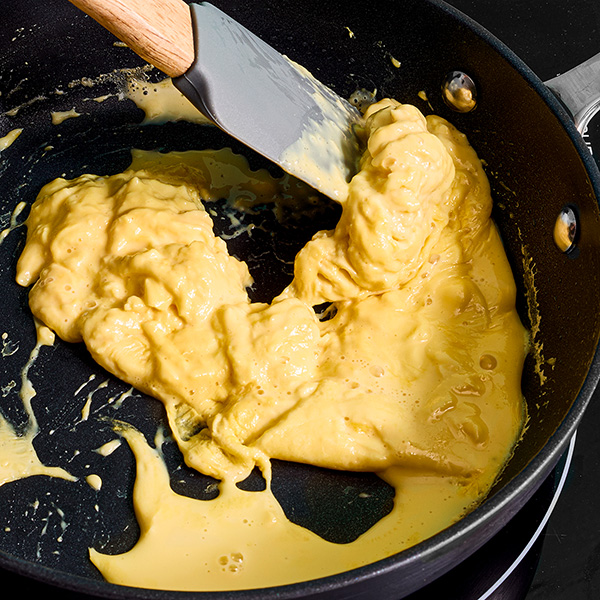

These plant-based eggs scramble almost like the real thing. Once food scientists get the texture right, they can begin to refine the flavor and nutritional content of the product.
CREDIT: EAT JUST, INC.
Those beany flavors aren’t caused by a single molecule, says Devin Peterson, a flavor chemist at Ohio State University: “It’s a combination that creates beany.” Protein extracts from legumes contain enzymes that create some of these off-flavor volatile molecules — and it’s a painstaking process to single out the offending volatiles and avoid or remove them, he says. (Presumably, cooking up single proteins in a vat could reduce this problem.) Many plant proteins also have molecules called polyphenols bound to their surfaces that contribute to beany flavors. “It’s very challenging to remove these polyphenols, because they’re tightly stuck,” says McClements.
Experts agree that eliminating beany and other off flavors is a good thing. But there’s less agreement on whether developers need to actively make a plant-based egg taste more like a real egg. “That’s actually a polarizing question,” says Jones.
Much of an egg’s flavor comes from sulfur compounds that aren’t necessarily pleasing to consumers. “An egg tastes a certain way because it’s releasing sulfur as it decays,” says Jones. When tasters were asked to compare Eat Just’s egg-free mayonnaise against the traditional, real-egg version, he notes, “at least 50 percent didn’t like the sulfur flavor of a true-egg mayo.”
That poses a quandary for developers. “Should it have a sulfur flavor, or should it have its own point of view, a flavor that our chefs develop? We don’t have an answer yet,” Jones says. Even for something like an omelet, he says, developers could aim for “a neutral spot where whatever seasoning you add is what you’re going to taste.”
As food technologists work to overcome these challenges, plant-based eggs are likely to get better and better. But the ultimate goal might be to surpass, not merely match, the performance of real eggs. Already, McClements and his colleagues have experimented with adding lutein, a nutrient important for eye health, to oil droplets in plant-based egg yolks.
In the future, scientists could adjust the amino acid composition of proteins or boost the calcium or iron content in plant-based eggs to match nutritional needs. “We ultimately could engineer something that’s way healthier than what’s available now,” says Bianca Datta, a food scientist at the Good Food Institute, an international nonprofit focused on advancing alternative proteins. “We’re just at the beginning of seeing what’s possible.”
Editor’s note: This article was updated November 20, 2024, to clarify the scope of activities supported by the Good Food Institute. Rather than solely promoting plant-based foods, as the article initially implied, it is more broadly interested in facilitating the development of alternative protein sources.
10.1146/knowable-111924-2
TAKE A DEEPER DIVE | Explore Related Scholarly Articles